News Blast: Your Daily Update
Stay informed with the latest news and trends.
Are You Protein-Obsessed? The Truth Revealed!
Discover the shocking truth behind protein obsession—are you getting enough or too much? Click to find out!
The Hidden Dangers of Excess Protein: What You Need to Know
The Hidden Dangers of Excess Protein can often be overlooked in the pursuit of fitness and health. Many individuals believe that increasing protein intake will solely lead to muscle growth and improved performance. However, consuming too much protein can put a strain on your kidneys, particularly for those with pre-existing conditions. Over time, this excess can lead to dehydration as your body works to eliminate the byproducts of protein metabolism. Additionally, the increased intake of protein-rich foods often means a decrease in the consumption of essential nutrients from fruits and vegetables, which can result in an unbalanced diet.
Another concern with high protein diets is their potential impact on bone health. While some studies suggest that protein is beneficial for maintaining bone density, excessive amounts can lead to calcium loss through urine. This can increase the risk of osteoporosis, especially in older adults. Moreover, many high-protein diets are rich in saturated fats and low in fiber, which can contribute to heart disease and digestive issues. It's crucial to find a balanced approach to protein consumption, aiming for moderation to avoid these hidden dangers while still reaping the benefits of this essential nutrient.
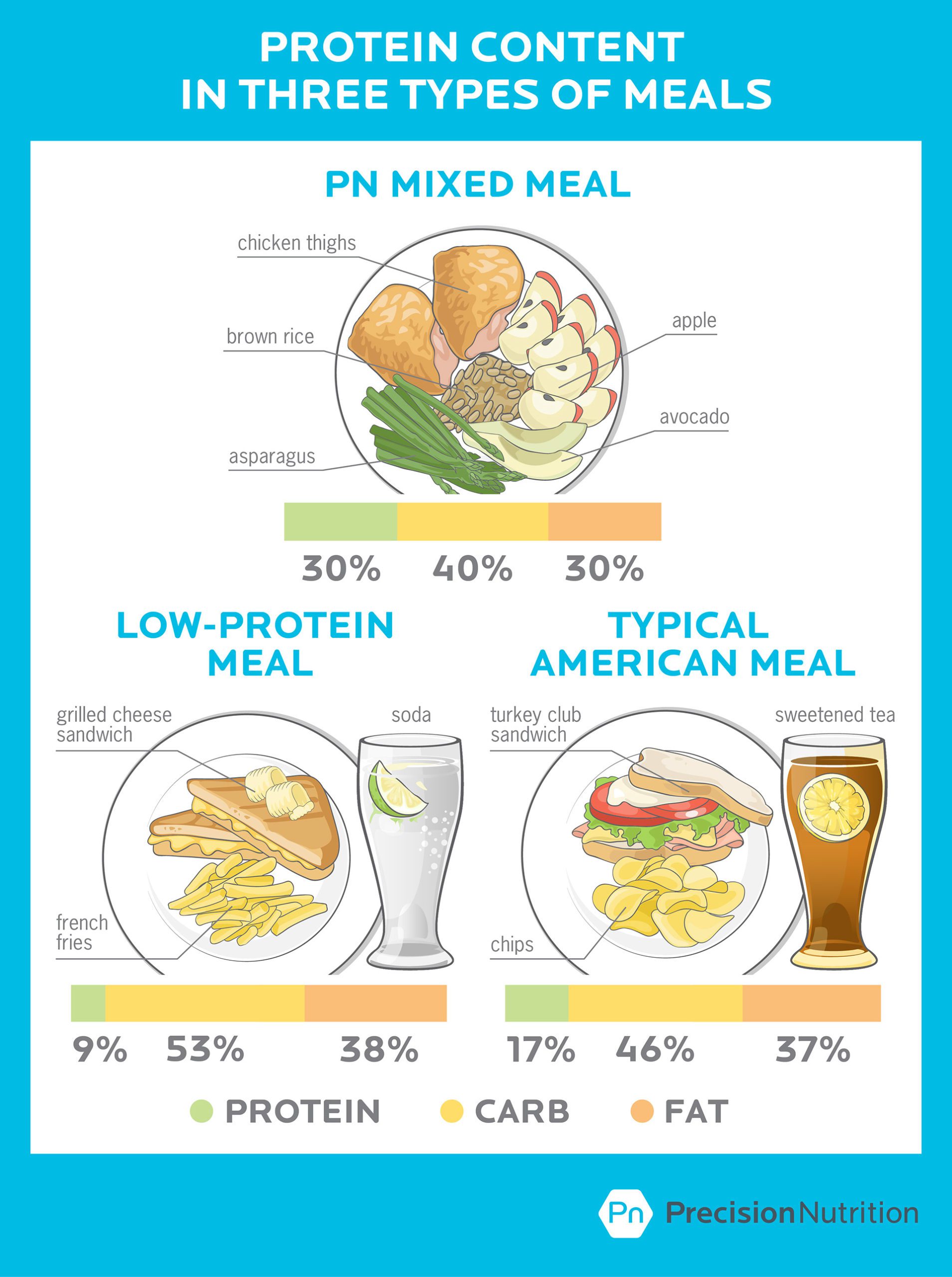
Are You Getting Enough Protein? Myths and Facts
When it comes to protein intake, there are many myths that can lead to confusion. One common misconception is that only athletes or bodybuilders need to prioritize their protein intake. In reality, protein is essential for everyone, as it plays a critical role in maintaining muscle mass, repairing tissues, and supporting overall health. While the recommended dietary allowance for adults is approximately 46 grams for women and 56 grams for men, individual needs may vary based on factors such as age, activity level, and health goals.
Another prevalent myth is that consuming high amounts of protein can harm your kidneys. This concern mostly applies to individuals with pre-existing kidney conditions; for healthy individuals, increasing protein intake is generally safe. Foods rich in protein, such as meat, dairy, eggs, legumes, and nuts, offer a plethora of health benefits beyond just muscle growth. To ensure you're getting enough protein, consider incorporating a variety of these sources into your daily meals.
How Much Protein Do You Really Need? A Deep Dive Into Your Diet
Understanding how much protein you really need is essential for optimizing your health and fitness goals. Protein is a crucial macronutrient that plays a pivotal role in repairing tissues, building muscles, and supporting overall bodily functions. The general recommendation for protein intake is about 0.8 grams per kilogram of body weight for sedentary adults. However, this number can vary based on factors such as age, activity level, and specific health goals. For instance, athletes or individuals engaging in intense workouts may require between 1.2 to 2.0 grams per kilogram to support muscle recovery and growth.
In addition to activity levels, it's important to consider your dietary preferences when assessing how much protein you really need. For instance, individuals following a vegetarian or vegan diet may need to focus on high-quality plant-based protein sources to meet their needs. Common protein sources include:
- Lean meats and poultry
- Fish and seafood
- Dairy products
- Legumes and beans
- Nuts and seeds
Maintaining a balanced diet that incorporates adequate protein can aid in weight management and enhance overall well-being, making it vital to assess and adjust your intake based on individual circumstances.