News Blast: Your Daily Update
Stay informed with the latest news and trends.
Clouds in the Sky or Clouds in the Server?
Explore the intriguing world of clouds—are they in the sky or in the server? Uncover the tech behind cloud computing and its real-life impacts!
Exploring the Differences: Clouds in the Sky vs. Clouds in the Server
Clouds in the sky and clouds in the server may share a name, but they serve vastly different purposes. The former consists of water vapor floating in the atmosphere, playing a crucial role in weather patterns and climate. These clouds can vary in type, including cumulus, stratus, and cirrus clouds, each contributing uniquely to the environment. Understanding the different types helps meteorologists predict weather changes, making this knowledge vital for daily life.
On the other hand, clouds in the server refer to cloud computing, a technology that allows data to be stored and accessed via the internet. This virtual form of storage offers scalability, flexibility, and collaborative features that are essential for modern businesses and individual users alike. With options such as public, private, and hybrid clouds, organizations can choose the level of security and control they need, making cloud computing an indispensable tool in today’s digital landscape.
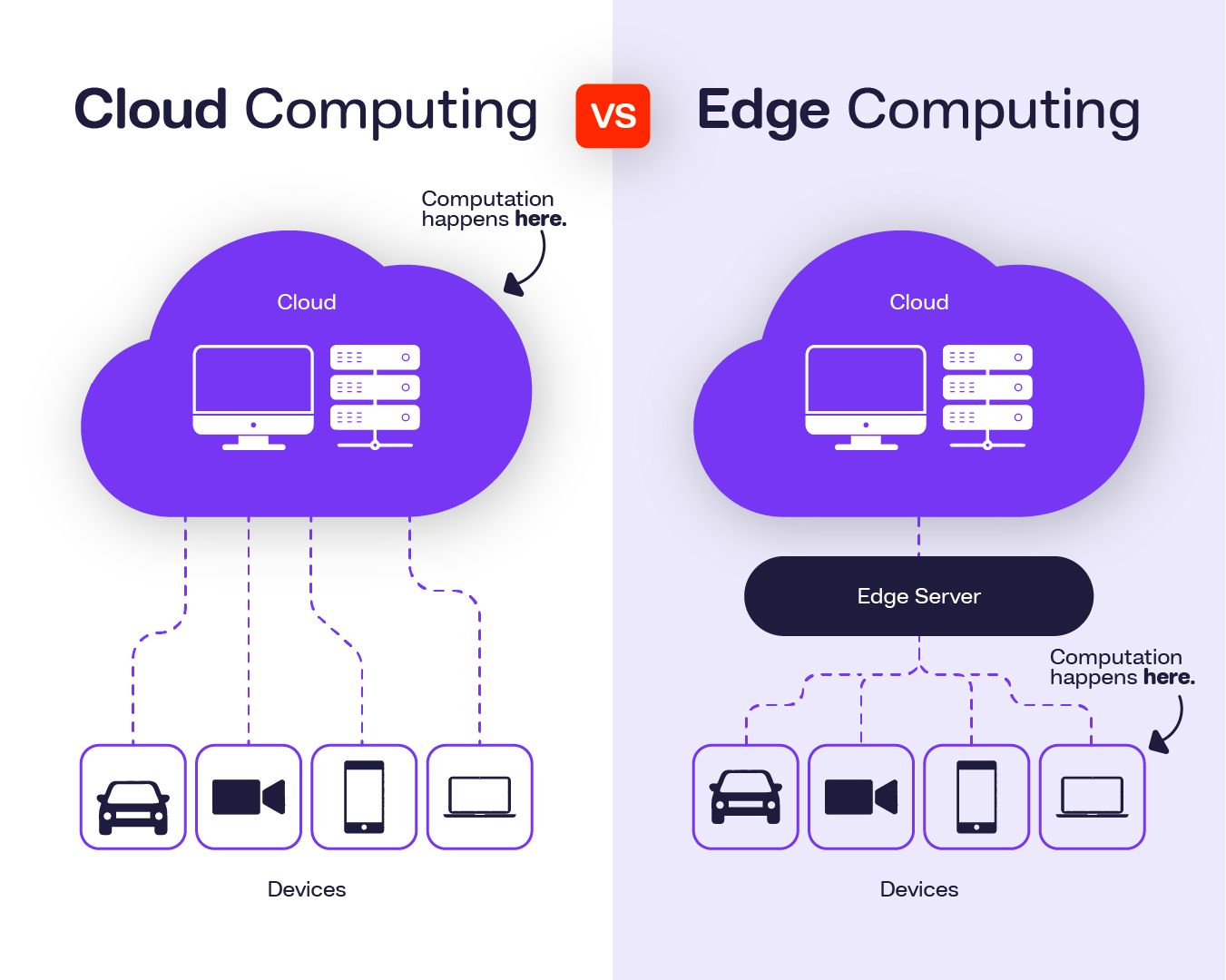
How Do Digital Clouds Function? A Deep Dive into Cloud Computing
Digital clouds function through a sophisticated network of servers, storage devices, and data centers that work collaboratively to provide on-demand computing resources over the internet. At its core, cloud computing allows users to access and store data remotely, rather than relying on local hardware. This architecture is typically divided into three key service models: Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS). Each of these models caters to different user needs, from basic resource provisioning to comprehensive application development environments.
The functionality of digital clouds is made possible through virtualization technology, which enables physical servers to be divided into multiple virtual servers. This not only optimizes the use of hardware but also enhances scalability, allowing businesses to adjust their resources according to demand. Additionally, cloud providers ensure high availability and reliability through redundant systems and data replication across multiple locations. As a result, even in the face of hardware failures or unexpected surges in traffic, users experience minimal disruption, making cloud computing an essential component of modern digital infrastructure.
What are the Environmental Impacts of Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing has transformed the way businesses and individuals store, process, and manage data, but it also comes with significant environmental impacts. One of the primary concerns is the energy consumption associated with data centers, which are essential for cloud services. According to estimates, these facilities consume approximately 1-2% of the world's total electricity, and as demand for cloud computing grows, so does the energy requirement. This energy consumption typically relies on non-renewable sources, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and climate change.
Additionally, the environmental footprint of cloud computing extends beyond energy usage. The manufacturing and disposal of hardware used in data centers, such as servers and cooling systems, lead to substantial electronic waste. Companies are now being urged to adopt more sustainable practices, such as using energy-efficient technologies and transitioning to renewable energy sources. Implementing these strategies not only mitigates the negative effects of cloud computing on the environment but also promotes a more sustainable digital future for all.