News Blast Hub
Stay updated with the latest news and insights.
When Currency Dances: A Trader's Balancing Act
Discover the thrilling world of currency trading! Uncover strategies to master the market's rhythm and achieve financial harmony.
Understanding Currency Pairs: The Heart of Forex Trading
Understanding currency pairs is essential for anyone looking to navigate the fascinating world of Forex trading. A currency pair consists of two currencies: the base currency and the quote currency. The first currency listed is known as the base currency, while the second is the quote currency. For example, in the currency pair EUR/USD, the Euro (EUR) is the base currency and the US Dollar (USD) is the quote currency. The value of the pair indicates how much of the quote currency is needed to purchase one unit of the base currency. This relationship is crucial for traders who aim to profit from fluctuations in currency values.
In Forex trading, currency pairs are generally categorized into three main types: major pairs, minor pairs, and exotic pairs. Major pairs are the most traded and include popular combinations like USD/JPY and GBP/USD. Minor pairs consist of less traded currencies, often excluding the US dollar, such as AUD/NZD and EUR/GBP. Lastly, exotic pairs involve a major currency paired with a currency from a developing economy, for instance, USD/THB (Thai Baht). Understanding these categories helps traders make informed decisions based on market trends and their personal risk tolerance.
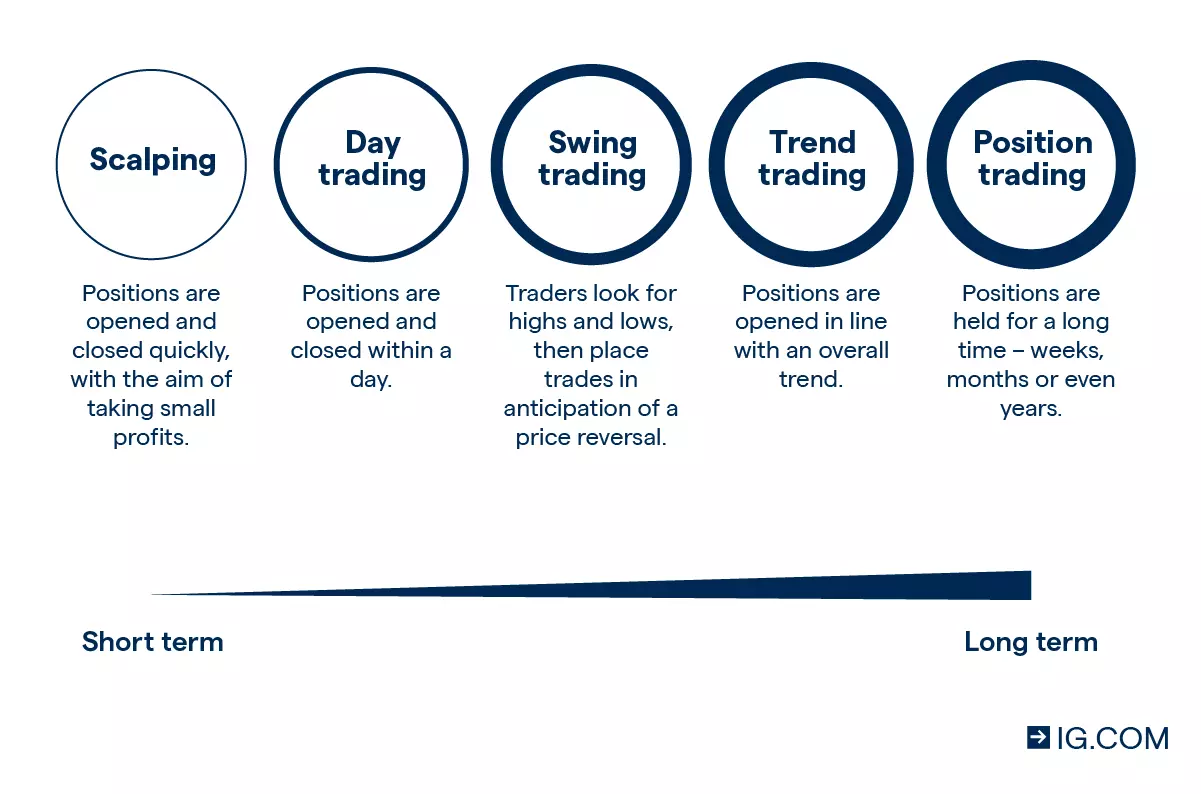
Top Strategies for Managing Risk in Forex Trading
Managing risk in Forex trading is crucial for maintaining profitability and safeguarding investments. One effective strategy is to use a proper risk-reward ratio. This involves assessing the potential gains against the possible losses before executing a trade. A commonly recommended ratio is 1:2, meaning for every dollar risked, the potential profit should be two dollars. Additionally, employing stop-loss orders can help traders minimize losses by automatically closing a position once it reaches a specified negative point, thereby preventing emotions from driving trading decisions.
Another essential strategy is to diversify your trading portfolio. Instead of concentrating on one currency pair, traders should consider spreading their investments across multiple pairs to mitigate risks associated with market volatility. This can be enhanced by using position sizing, which involves determining the number of units to trade based on account size and risk tolerance. By following these strategies, traders can significantly reduce their exposure to market fluctuations, allowing for better management of risk in the ever-evolving world of Forex trading.
How Economic Indicators Influence Currency Movements
The relationship between economic indicators and currency movements is a fundamental aspect of Forex trading. Economic indicators, such as GDP growth rates, unemployment figures, and inflation levels, serve as key signals that investors and traders use to gauge the health of a country's economy. For instance, a higher-than-expected GDP growth rate typically strengthens a country's currency, as it reflects robust economic performance and can lead to increased interest rates. Conversely, negative economic data, such as rising unemployment rates or decreasing manufacturing output, may weaken a currency as investor confidence wanes.
Additionally, central banks closely monitor these economic indicators when making monetary policy decisions. Central banks use interest rate adjustments to either stimulate economic growth or control inflation. For example, if inflation is rising, a central bank may decide to increase interest rates, which often leads to a stronger currency as foreign investors seek higher returns. The anticipation of these decisions can also cause fluctuations in currency values ahead of official announcements, showcasing how interconnected economic indicators and currency movements are within the global market.